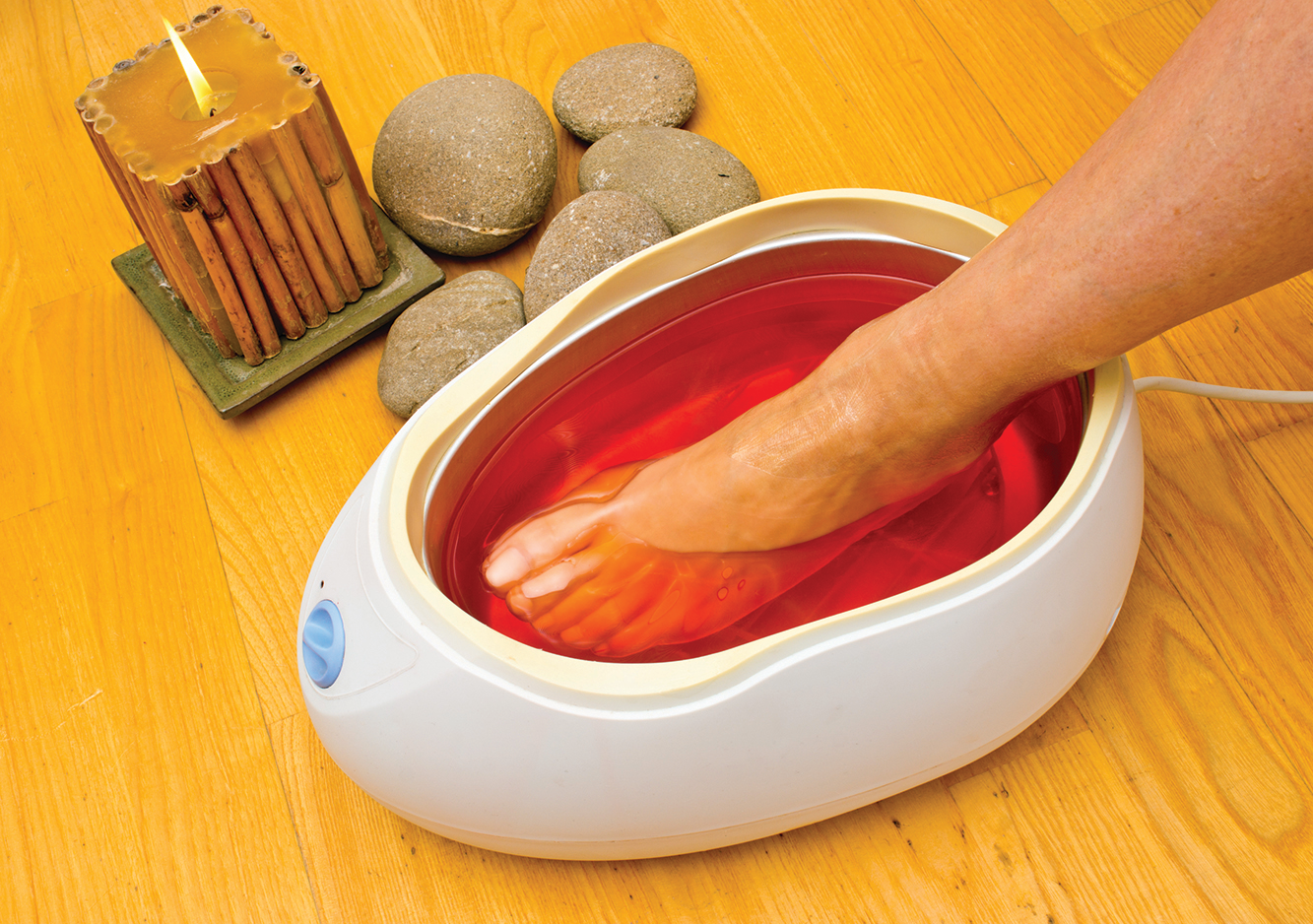
Chemical structure of paraffin wax (A), m-xylene (B) and n-heptane (C)
Download scientific diagram | Chemical structure of paraffin wax (A), m-xylene (B) and n-heptane (C), and their corresponding space-fi lling molecular models from HyperChem 8 software (A ' , B ' , and C ' , respectively). Paraffin wax is the aliphatic chain, C 16 H 34 , and commercial xylene is a mixture of the three aromatic isomers ( o-, m-, and p-); the p-isomer is the predominant form (Windholz 1983). from publication: Replacing xylene with n -heptane for paraffin embedding | Abstract In standard histological technique, aromatic solvents such as xylene and toluene are used as clearing agents between ethanol dehydration and paraffin embedding. In addition, these solvents are used for de-waxing paraffin sections. Unfortunately, these solvents are | Xylenes, Solvents and Toluene | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
What is paraffin by organic chemistry? - Quora

PDF) Replacing xylene with n -heptane for paraffin embedding

Enhanced separation for paraffin wax using CO2-responsive emulsions based on switchable hydrophilicity solvents - ScienceDirect
Hydrocarbons and Lipids: An Introduction to Structure, Physicochemical Properties, and Natural Occurrence

Begoña LÓPEZ-ARIAS, PostDoc Position, PhD Genetics and Cell Biology, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Madrid, UAM, Department of Biology

Effects of Waxes and the Related Chemicals on Asphaltene Aggregation and Deposition Phenomena: Experimental and Modeling Studies
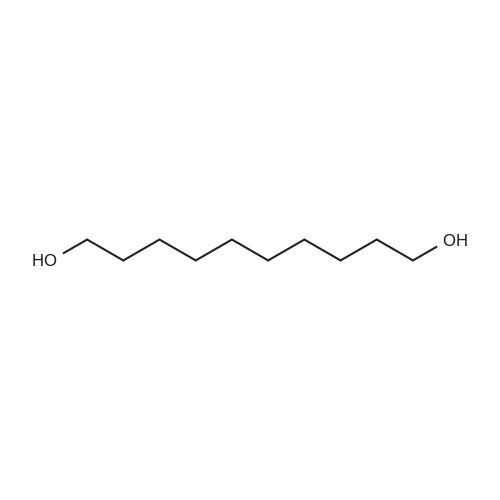
112-47-0, 1,10-Decanediol

Chemical structure of paraffin wax (A), m-xylene (B) and n-heptane (C)

Paraffin wax

US11261151B2 - Methods for making and using endoxifen - Google Patents

Chemical structure of paraffin wax (A), m-xylene (B) and n-heptane (C)









