Polymorph screening in pharmaceutical development - European Pharmaceutical Review
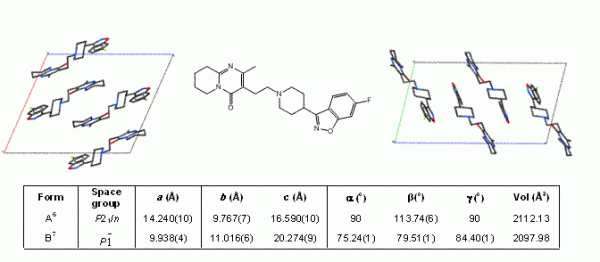
The majority of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are produced by crystallisation and so the phenomenon of polymorphism, whereby an organic molecule can adopt more than one crystalline form (Figure 1), is of considerable importance when trying to achieve consistent product quality during the manufacture of pharmaceutical solids and solid dosage forms. Although morphology and particle size-distribution are important solid-state characteristics, the uncontrolled occurrence of multiple physical forms (polymorphs, solvates, salts, co-crystals or amorphous) of an API can have significant effects on the performance of the material during processing, manufacture, storage and administration. For example, the solubility difference between some polymorphs has been shown to be over four times that of the least soluble form1 and can vary by significantly more for amorphous forms2.
Pharmaceutical QbD: Omnipresence in the product development lifecycle

Computational polymorph screening reveals late-appearing and

Minimizing Polymorphic Risk through Cooperative Computational and

Streamline end-to-end drug development and manufacturing
Pharmaceutics, Free Full-Text
Polymers, Free Full-Text

Drug Polymorphism: A Key Consideration for API Development - Xtalks
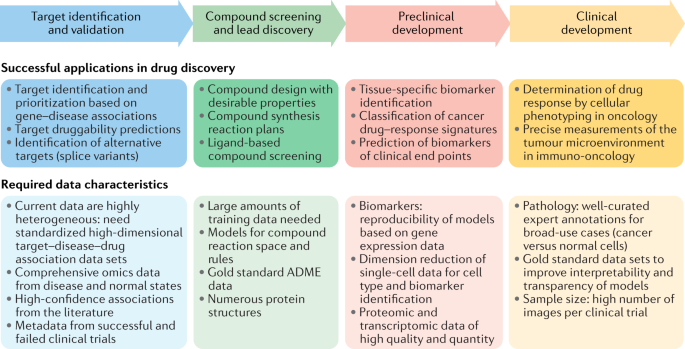
Applications of machine learning in drug discovery and development

Packing Polymorphism Affecting the Optoelectronic Properties of a

Pharmaceutics, Free Full-Text









